In slope protection engineering, geogrids and geotextiles do not function independently. Through the collaborative mode of “structural constraints+functional complementarity”, the two construct an integrated protection system of “stability anti-seepage drainage ecology”, which solves the problems of weak anti sliding ability, soil erosion, and difficult ecological restoration of single material protection. It is suitable for complex scenarios such as highway, railway, water conservancy, and mining slopes, and is an efficient and economical combination solution in current slope protection engineering.
1、 Core Collaborative Logic: From “Single Protection” to “System Reinforcement”
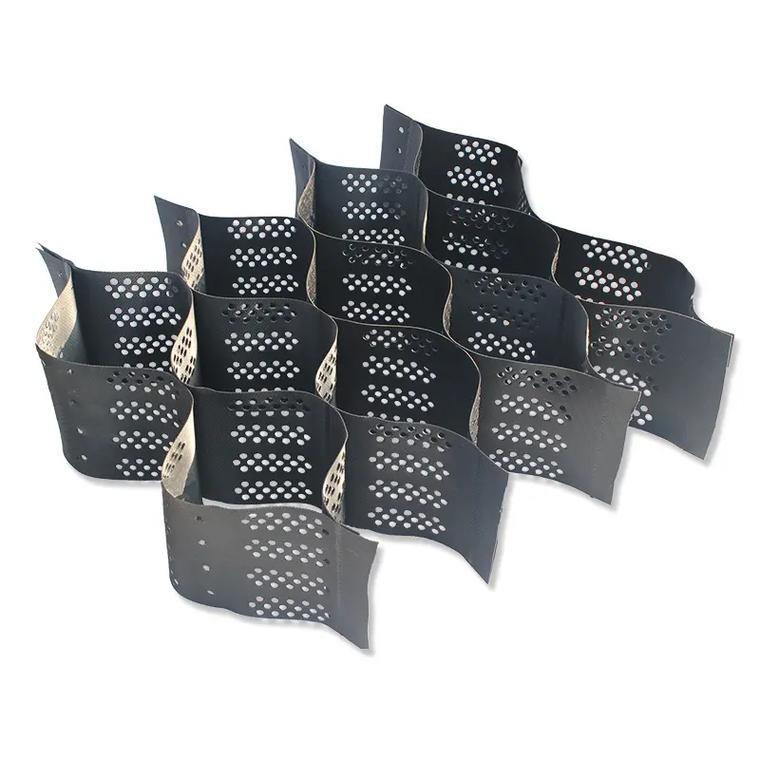
The core function of the geogrid is to provide structural constraints and overall stability of the slope. By using a three-dimensional grid structure to lock in the slope filling materials (soil, sand and gravel), the displacement of the filling materials is limited, and the slope’s resistance to sliding and erosion is improved; The core function of geotextile is functional protection and ecological adaptation. Through filtration, anti-seepage, drainage, and soil conservation functions, it solves the problems of water pressure and soil erosion inside the slope, while providing basic conditions for vegetation growth. The essence of the collaboration between the two is to build a “skeleton” in the geogrid, fill the “flesh and blood” with geotextile, and form a dual guarantee of “hard support+soft protection”, which not only solves the short-term stability problem of the slope, but also achieves long-term ecological restoration and protection durability.
2、 Specific synergies and technical details (scenario analysis)
(1) Anti slip stability synergy: enhancing the bearing capacity and displacement resistance of slopes
1. The “locking” function of the geogrid: After the geogrid is unfolded, it forms a honeycomb shaped three-dimensional grid. When laid on the slope surface or inside the slope body, the grid forms a interlocking structure with the filling material (soil, gravel), transforming the loose filling material into a composite soil with strong integrity, significantly improving the internal friction angle and cohesion of the slope body, and preventing the slope body from sliding along the sliding surface. Especially for gentle slopes (with a gradient of 1:1.5~1:2.5) or stone filled slopes, geogrids can increase the anti sliding force of the filling material by 30%~50%, avoiding local collapse.
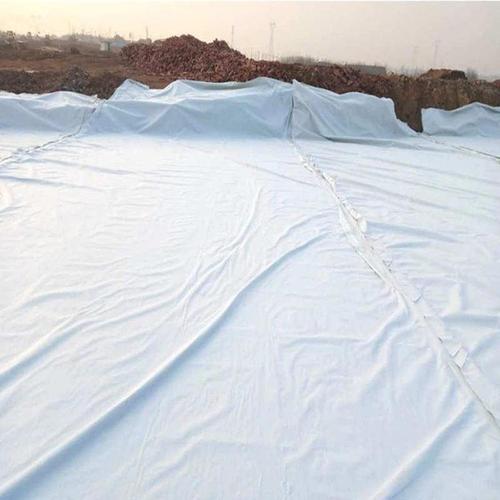
2. “Laying” and “reinforcement” assistance of geotextile: laying geotextile (usually short fiber needle punched non-woven geotextile) under the geotextile compartment can reduce the friction loss between the geotextile compartment and the slope foundation soil, and protect the compartment material (avoid being scratched by sharp stones); On the other hand, the fiber structure of geotextile can form a composite layer with the foundation soil and grid filling, enhancing the overall integrity of the slope surface, preventing local settlement of the foundation soil below the grid due to water flow erosion or load, and further strengthening the locking effect of the geotextile grid.
3. Collaborative advantages: The combination of the two can solve the problems of “weak connection between the grid and the foundation soil” and “loose local filling materials” in the protection of a single geotechnical grid, while compensating for the weak tensile and displacement resistance of the geotextile itself, improving the overall anti sliding stability of the slope by more than 60%. It is suitable for the reinforcement of high and steep slopes (slope ≤ 1:1.2) or soft soil foundation slopes.
(2) Collaborative anti-seepage and drainage: solving the problems of slope water pressure and soil erosion
One of the core causes of slope instability is excessive water pressure inside the slope (rainwater infiltration, groundwater accumulation), as well as soil erosion caused by rainwater erosion on the slope surface. The coordination between geogrid and geotextile can form a closed-loop protection of “anti-seepage+drainage+filtration”:
1. The dual function of “filtration drainage” of geotextile:
◦ Filtration function: Use non-woven geotextiles with good permeability (permeability coefficient ≥ 1 × 10 ⁻ cm/s) to lay on the slope surface. When rainwater washes, the geotextile can intercept soil particles (prevent soil erosion), while allowing rainwater to penetrate into the interior of the slope to avoid runoff erosion;
Drainage function: Lay geotextile (or composite geomembrane) in the drainage blind ditch and seepage ditch inside the slope, and cooperate with the grid channels of the geogrid to form a “horizontal vertical” drainage network, quickly discharge the accumulated water inside the slope, reduce pore water pressure, and avoid slope swelling and collapse caused by excessive water pressure.
2. “Water diversion” and “anti-seepage assistance” of geogrids:
◦ Water diversion function: The grid channels of the geogrid can serve as slope drainage channels, guiding rainwater on the slope to flow along the grid channels to the slope bottom drainage system, avoiding rainwater from being trapped on the slope and forming concentrated erosion;
◦ Anti seepage assistance: For slopes with high moisture content (such as water conservancy slopes and areas with frequent rainy seasons), a composite geomembrane (anti-seepage type) can be added between the geocell and the geotextile. The geocell serves as a protective layer to prevent the composite geomembrane from being scratched by the slope filling material. At the same time, the geotextile (filtering type) is laid on the outside of the composite geomembrane to achieve the triple protection of “anti-seepage+filtration+drainage”, completely solving the problem of water accumulation inside the slope.
3. Collaborative advantages: It can effectively control the moisture content of the slope, reduce the softening effect of water on the slope (especially for cohesive soil slopes), reduce slope erosion caused by rainwater erosion, reduce soil erosion on the slope by more than 80%, and avoid deformation of the geogrid and loss of filling materials caused by water pressure, extending the service life of the protective system (from 5-8 years for a single material to 15-20 years).
(3) Ecological Restoration Collaboration: Achieving the Unification of “Engineering Protection” and “Ecological Greening”
Modern slope protection engineering has shifted from “hard protection” to “ecological protection”, and the coordination between geogrids and geotextiles is the core technology combination of ecological slope protection:
1. The role of the “grass planting foundation bed” in the geogrid: After the geogrid is laid, the grid is filled with planting soil (or nutrient soil) to form a stable grass planting foundation bed, avoiding the loss of planting soil under rainwater erosion. At the same time, the grid structure can fix grass seeds or vegetation roots, preventing vegetation from collapsing due to slope sliding. For rock slopes or barren slopes, geogrids can serve as “soil carriers” to provide space for vegetation growth.
2. Ecological assistance of “soil and water retention” of geotextile: Before filling the planting soil in the geogrid, short fiber needle punched geotextile is laid at the bottom of the grid to prevent mixing of planting soil with the slope base soil and ensure the fertility of the planting soil; On the other hand, the water retention performance of geotextiles can reduce the evaporation of planting soil moisture, while allowing rainwater to slowly infiltrate, providing sufficient water for vegetation roots and promoting vegetation growth. In addition, the flexible structure of geotextiles can adapt to the growth and extension of vegetation roots, avoiding damage to the roots by rigid materials such as geogrids.
3. Collaborative advantage: The combination of the two can achieve synchronous implementation of “engineering reinforcement+ecological greening”, solving the problems of poor ecological performance of a single geogrid (only able to fix soil, difficult to plant grass) and easy loss of grass when planted with a single geotextile (without structural constraints). After the vegetation grows, the root system forms a composite protective layer of “root grid geotextile” with the geogrid and geotextile, further enhancing the stability of the slope, achieving slope greening, improving the ecological environment, and suitable for ecological protection engineering of highway and railway slopes.
(4) Synergistic erosion resistance and durability: enhancing the long-term reliability of the protective system
1. Slope erosion resistance synergy: The erosion of slopes by rainwater or water flow is mainly divided into “slope erosion” and “gully erosion erosion”. The grid structure of the geogrid can disperse the water flow velocity (reducing it by 40%~60%) and reduce the impact force of water flow on the slope surface; The geotextile directly covers the slope surface to prevent the direct erosion of soil by water flow. At the same time, it can prevent the loss of soil particles through filtration. Together, the geotextile can effectively resist the rainstorm (rainfall ≥ 50mm/h) or strong erosion of water flow, and avoid the formation of gullies on the slope surface.
2. Material durability synergy: Geocell (mostly made of HDPE) has anti-aging and anti-corrosion properties, but it is prone to aging after long-term exposure to ultraviolet light or high temperature environment; Geotextiles, especially needle punched non-woven geotextiles, have good resistance to ultraviolet radiation and acid alkali corrosion. When laid on the surface or inside of geotextile compartments, they can effectively block ultraviolet radiation and reduce the aging rate of compartment materials; At the same time, the geogrid can protect the geotextile from external forces such as stone impact and construction machinery rolling, extending the service life of the geotextile. The synergy between the two can enhance the durability of the protective system to over 20 years, far exceeding the service life of a single material.
3、 Key technologies for collaborative construction (ensuring maximum effectiveness)
1. Laying sequence and layer design: The core sequence is “slope trimming → laying bottom layer geotextile (filter type) → laying geogrid chamber → filling material (or planting soil) → laying surface layer geotextile (protective type) → fixed compaction”. The bottom layer geotextile needs to be tightly adhered to the slope, and the geogrid is fixed to the slope through anchor rods (or U-shaped nails) to ensure that the grid is flat and wrinkle free; The surface geotextile should cover the edges of the geogrid to prevent the loss of edge fillers.
2. Material selection matching:
Geotechnical grid cell: Select according to the slope gradient and filling material type. For gentle slopes (≤ 1:2), select grid cells with a height of 50-100mm, and for steep slopes (1:1.2~1:1.5), select grid cells with a height of 100-150mm. HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is preferred as the material, with a tensile strength of ≥ 12kN/m and a weld strength of ≥ 8kN/m.
Geotextile: The bottom layer is made of short fiber needle punched non-woven geotextile (weight 200-300g/㎡, fracture strength ≥ 15kN/m), used for filtration and soil protection; The surface layer is made of long filament spunbond non-woven geotextile (weight 300-400g/㎡, fracture strength ≥ 20kN/m), used for anti erosion and protection; Composite geomembrane (geotextile+PE membrane, membrane thickness ≥ 0.5mm, permeability coefficient ≤ 1 × 10 ⁻¹⁰ cm/s) is selected for anti-seepage scenarios.
3. Connection and fixing details: The overlap width between geogrids should be ≥ 100mm, and they should be fixed by welding or bolts; The overlap width between geotextiles shall be ≥ 200mm (in the direction of water flow), and shall be connected by sewing or hot melting; At the top, bottom, and corners of the slope, the geocell and geotextile should extend to at least 500mm outside the top of the slope and be fixed with anchor rods or roof stones to prevent the edges from lifting or being washed away by water flow.
4、 Summary of Applicable Scenarios and Collaborative Advantages
Applicable scenarios, collaborative core advantages, single material defects
Reinforcement of high and steep slopes (slope ratio 1:1.2~1:1.5) using geogrid locking fillers and geotextile bedding to enhance anti sliding stability and avoid local collapse. Geogrid: poorly connected with foundation soil; Geotextile: weak displacement resistance
Geotextile anti-seepage and drainage for water conservancy slopes (reservoirs, rivers)+geogrid water diversion protection to reduce water pressure and prevent slope softening. Geogrid: no anti-seepage function; Geotextile: weak erosion resistance
Ecological slope protection (highway, railway) geogrid planting grass foundation bed+geotextile to protect soil and water, achieving the unity of engineering protection and ecological greening. Geogrid: without water retention function, vegetation is prone to withering; Geotextile: Grass planting is prone to loss
Geotextile chambers for rock filled slopes/soft soil foundation slopes constrain the use of rock filled materials and geotextile filtering for leveling, enhancing the overall integrity of the slope and avoiding settlement. Geotextile chambers: Rock filled materials are prone to loosening; Geotextile: Without structural constraints
5、 Key considerations (avoid collaborative failure)
1. Material selection needs to be matched: It is strictly prohibited to use low strength geogrids (tensile strength<10kN/m) or low weight geotextiles (<200g/㎡), otherwise it will lead to insufficient strength of the collaborative system and cause protection failure.
2. Construction quality control: The geogrid should be laid flat to avoid wrinkles (wrinkles can cause local stress concentration and damage to the grid); The laying of geotextile should be free of damage and leaks (leaks can cause filtration failure and soil erosion).
3. Post maintenance: Regularly check the integrity of the welding points and geotextiles in the geocell, and promptly repair damaged parts; For ecological slope protection, regularly replenish water and vegetation to ensure a close connection between the root system and the protective system.
VI. Summary
The synergy between geogrid and geotextile in slope protection engineering is a perfect combination of “structural mechanics” and “functional protection”. Through the multidimensional synergy of “locking filtering anti-seepage drainage ecology”, it not only solves the short-term stability problem of slopes, but also achieves the unity of long-term protection and ecological restoration. Its protective effect is far superior to that of a single material. In practical engineering, it is necessary to scientifically select materials and standardize construction processes based on slope gradient, geological conditions, hydrological environment, and ecological needs, in order to fully leverage the synergistic advantages of the two and ensure the stability, durability, and ecology of slope engineering.
Post time: Dec-22-2025