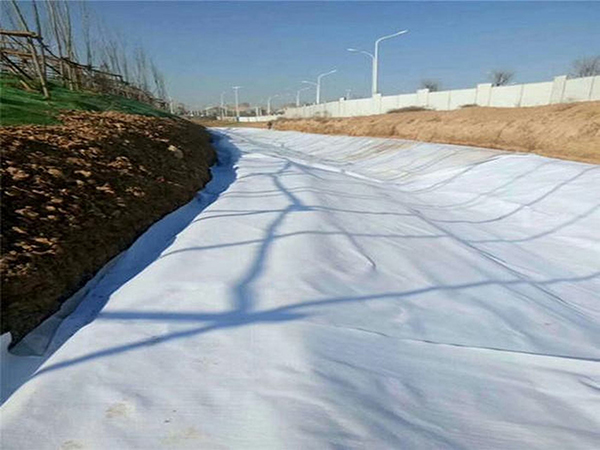
Geotextile, as a permeable geosynthetic material made from polymer fibers through weaving, needle punching, hot melt and other processes, plays the role of an “all-around player” in various engineering constructions. Its core role can be summarized as the following key aspects:
1、 Filtering and isolation: building a strong “protective line” for engineering structures
In water conservancy, transportation, environmental protection and other engineering projects, the filtering and isolation functions of geotextiles are the basic guarantee.
• Filtering function: When water flows through the soil, geotextile can effectively block the loss of soil particles, while allowing water infiltration, avoiding damage such as “pipe surge” and “soil flow” caused by water erosion. For example, in dam construction, laying geotextile between the dam body and foundation can facilitate the smooth discharge of groundwater, prevent sediment from flowing away with water flow, and maintain the stability of the dam body.
Isolation function: By separating soil with different properties (such as sand and clay) or soil from other materials (such as gravel, concrete), it avoids material mixing due to stress or environmental effects, which may affect engineering performance. For example, in the construction of highway subgrade, geotextile can isolate the subgrade filling from the soft soil of the foundation, prevent the filling from sinking and mixing into the soft soil layer, ensure uniform stress on the subgrade, and extend the service life of the road.
2、 Drainage and Water Diversion: Building an Engineering System “Microcirculation”
The porous structure of geotextile makes it an efficient “drainage channel”, especially in projects that require water diversion, with significant advantages.
Rapid drainage: In underground drainage systems, tunnel anti-seepage drainage, landfill leachate collection and other scenarios, geotextiles can timely capture and conduct moisture, reduce soil pore water pressure, and avoid damage to structures such as softening and expansion caused by accumulated water. For example, laying geotextile under the railway subgrade can quickly drain rainfall or groundwater, prevent the roadbed from settling and turning over due to long-term immersion, and ensure the safety of railway operation.
• Water diversion and confluence: When used in conjunction with drainage pipes, geotextiles can guide water flow towards designated drainage facilities, forming a complete drainage network. In slope protection engineering, geotextile is laid between the vegetation layer and the rock layer, which can collect rainwater infiltration water and guide the water to the drainage ditch at the bottom of the slope, reducing water erosion and potential landslide risks on the slope.
3、 Reinforcement and Protection: Enhancing the ‘Bearing Capacity’ of Engineering Structures
The high-strength fiber structure of geotextile endows it with reinforcement and protective functions, which is an important means to improve engineering stability.
• Reinforcement effect: By being laid in the soil, geotextiles utilize the tensile strength of fibers to generate friction and embedding with the soil, restraining soil deformation and enhancing the shear strength and overall stiffness of the soil. In engineering projects such as retaining walls, embankments, and soft soil foundation treatment, geotextiles are used as reinforcement materials to reduce lateral displacement of soil, decrease foundation settlement, and improve the structural bearing capacity. For example, in the soft foundation treatment of highways, after laying a geotextile reinforcement layer, the bearing capacity of the foundation can be increased by 30% to 50%, effectively reducing the risk of pavement cracking.
• Protective function: As a surface protective layer, geotextile can cushion external impact and protect the underlying materials from damage. In river slope protection, geotextile is laid under the slope protection stones or concrete slabs to reduce the erosion of water flow on the foundation soil of the slope protection, while preventing the loss of small particles between the stones and maintaining the integrity of the slope protection structure; In landfills, geotextiles can protect the anti-seepage membrane from sharp gravel punctures and extend the service life of the anti-seepage system.
4、 Anti seepage and anti filtration: strictly adhere to the “safety control” of the engineering environment
In projects with high requirements for anti-seepage such as environmental protection and water conservancy, geotextile is combined with other materials to form a reliable anti-seepage barrier.
Composite anti-seepage: Combined with anti-seepage materials such as HDPE film, geotextile can serve as upper and lower protective layers. On the one hand, it prevents the membrane material from being punctured by sharp impurities in the soil, and on the other hand, it evenly transmits soil stress, avoiding damage to the membrane material due to excessive local stress. Together, they form an efficient anti-seepage system, which is widely used in landfill sites, sewage treatment tanks, artificial lakes and other projects to prevent pollutant leakage from polluting groundwater and soil.
Anti filter protection: In drainage blind ditches, pressure relief wells and other facilities, geotextile serves as an anti filter layer, which can not only allow water flow to enter the drainage body smoothly, but also prevent soil particles from entering the pipeline or well, avoiding blockage and ensuring the long-term effective operation of the drainage system. In agricultural water conservancy projects, geotextile wrapped drainage pipes can prevent sediment accumulation in pipelines, maintain smooth drainage in farmland, and improve soil salinization problems.
5、 Environmental Protection and Ecology: Supporting the Sustainable “New Path” of Engineering
With the popularization of green engineering concepts, the environmental and ecological functions of geotextiles are increasingly prominent.
Ecological restoration: In slope greening and river ecological management, geotextile can serve as a “carrier” for vegetation growth. Its porous structure provides attachment space and water conservation for plant roots, while fixing the surface soil to prevent soil erosion and promote rapid vegetation recovery, achieving coordination and unity between engineering protection and ecological environment. For example, in mine restoration, planting grass seeds after laying geotextile can accelerate the formation of slope soil and reduce the risk of dust and debris flow on exposed mountains.
Material recycling: Modern geotextiles are often made of recyclable materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene. Some products have degradation properties, reducing the consumption of traditional engineering materials such as sand and concrete, lowering carbon emissions, and meeting the requirements of circular economy and sustainable development.
From transportation infrastructure to water conservancy projects, from environmental protection facilities to ecological restoration, geotextile permeates every aspect of engineering construction with its multifunctionality. It is not only the “guardian” of structural stability, but also the “barrier” of environmental safety, and the “practitioner” of green engineering. With the continuous advancement of material technology, the performance of geotextiles will continue to be optimized, playing an irreplaceable role in more complex engineering scenarios, and safeguarding the safety, efficiency, and sustainable development of modern engineering construction.
Post time: Jun-09-2025