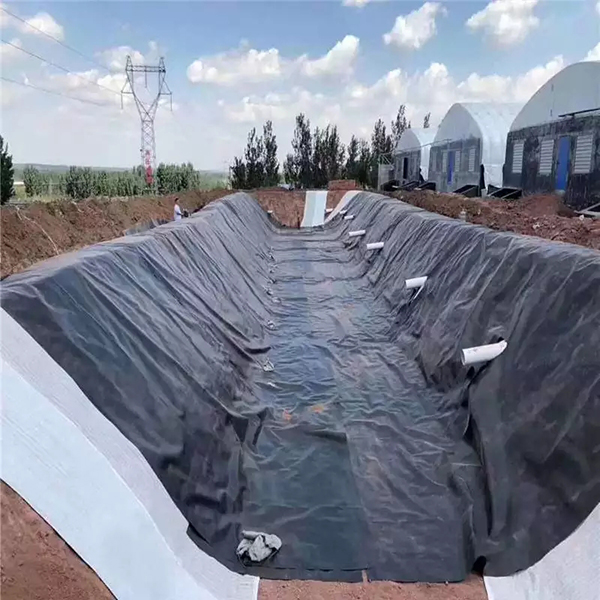
In the field of ecological governance and engineering protection, geomembrane, as a polymer synthetic material, has become a key material for solving core problems such as water resource protection, environmental pollution control, and engineering safety protection due to its excellent anti-seepage, isolation, and reinforcement properties. Its position has become increasingly prominent with the upgrading of governance needs.
The ‘anti-seepage core’ in water resource management
In water resource development and protection engineering, geomembrane is the core carrier to ensure efficient utilization of water bodies and ecological balance. In large-scale water conveyance channels, reservoirs, lakes and other projects, traditional soil materials for anti-seepage are prone to leakage due to geological settlement and water flow erosion, while geomembranes can control the leakage rate below 0.1% through a continuous and complete anti-seepage layer, significantly improving water resource utilization efficiency. For example, in the South to North Water Diversion Middle Route Project, a composite geomembrane anti-seepage system is used along the channel, reducing leakage by over 1 billion cubic meters annually and ensuring water supply stability; In the construction of reservoirs in arid areas, geomembranes can effectively lock in surface water, providing a basic guarantee for agricultural irrigation and ecological replenishment, and becoming a “necessary material” for the management of water scarce areas.
Isolation Barrier in Environmental Pollution Control
In the fields of environmental protection such as solid waste treatment and soil remediation, geomembranes are the “first line of defense” to block the spread of pollution. In municipal solid waste landfill and hazardous waste disposal projects, geomembranes can withstand corrosive leachate such as strong acids and alkalis through multi-layer composite structures (such as high-density polyethylene film combined with geotextiles), preventing harmful substances from infiltrating soil and groundwater. Data shows that landfill sites using geomembranes can reduce the risk of groundwater pollution in the surrounding area by over 90%. In addition, in the restoration of industrial sites and the control of heavy metal pollution in mining areas, geomembranes can construct a closed anti-seepage system, combined with leaching, bioremediation and other technologies, to control the spread of pollution and provide a controllable environment for soil restoration. They are key supporting materials for the “simultaneous treatment and prevention” of polluted sites.
The ‘cornerstone of stability’ in engineering safety protection
In the safety protection of transportation, municipal, water conservancy and other engineering projects, geomembranes significantly improve the durability of structures through isolation and reinforcement. In the construction of highway and railway subgrade, geomembranes can isolate the subgrade from the base soil material, avoiding subgrade softening and settlement caused by rainwater infiltration, and extending the service life of the project; In dam and slope protection engineering, the reinforced structure formed by the combination of composite geomembrane and soil material can enhance the shear strength of soil and reduce the risk of disasters such as landslides and collapses. For example, in the reinforcement project of the Yangtze River embankment, the combination of geomembrane and impermeable wall was adopted, which effectively solved the problem of seepage in the embankment and improved the flood control standards.
Functional regulators in ecological restoration
In the fields of wetland restoration and river ecological governance, geomembranes are the “invisible regulators” for rebuilding ecosystems. In the construction of artificial wetlands, geomembranes can be designed with permeability coefficients based on ecological needs to control water exchange rates and create suitable habitats for aquatic organisms; In river ecological revetment engineering, it can prevent soil erosion on the bank slope and maintain the connection between groundwater and river water through reserved seepage channels, achieving a balance between ecological and protective functions.
In summary, geomembranes are not only the core material for technical implementation in the field of governance, but also the key link between engineering safety and ecological protection. Their application runs through multiple links such as water resource utilization, pollution prevention and control, engineering protection, and ecological restoration, and has become an indispensable and important component of the modern governance system.
Post time: Jul-21-2025