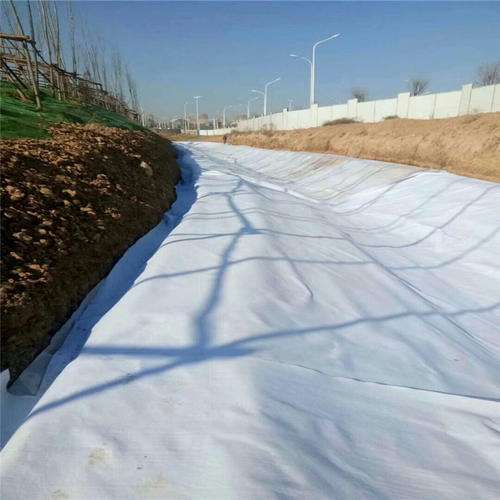
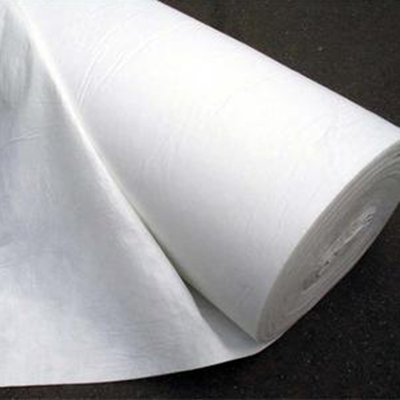
Geotextile is a permeable geosynthetic material made of synthetic fibers through needle punching or weaving, which combines flexibility and durability. It is widely used in various engineering fields such as water conservancy, highways, railways, and environmental protection. Its core functions revolve around five directions: anti-seepage, drainage, isolation, reinforcement, and protection, providing key guarantees for the stability and service life of engineering structures.
The anti-seepage function is one of the fundamental applications of geotextiles, often combined with geomembranes to form anti-seepage composite geotextiles. In water conservancy dams, artificial lakes, reservoirs and other engineering projects, it can effectively prevent water leakage, while relying on its own breathability to avoid pressure damage caused by water accumulation under the membrane. It is particularly suitable for anti-seepage treatment in special geological environments such as saline alkali land and swamps, reducing the risk of water loss and soil salinization.
The drainage function relies on the porous structure of geotextiles, whose fiber gaps can not only allow water to quickly penetrate, but also intercept soil particles. In the construction of highway subgrade and railway track bed, geotextile can timely discharge the accumulated water in the soil, reduce pore water pressure, prevent subgrade softening and settlement, and ensure the long-term stability of transportation engineering; In slope greening and landfill engineering, it can also accelerate soil drainage, avoid plant root rot and landfill leachate accumulation.
The isolation function is reflected in the layered processing of materials with different materials and particle sizes, which can prevent the deterioration of engineering performance caused by material mixing. For example, in highway engineering, geotextile is laid between the roadbed and the pavement, which can isolate crushed stone aggregates and roadbed soil, avoiding soil particles from entering the aggregate layer and affecting the pavement bearing capacity; In the filling project, the backfill soil can be isolated from the undisturbed soil to prevent the mixing of different soil layers and ensure the uniformity of the compactness of the filling structure.
Reinforcement and strengthening functions are the core values of geotextiles in geotechnical engineering, which enhance the shear strength of soil through friction and tensile properties with the soil. In the treatment of soft soil foundation, geotextile can disperse the upper load and reduce the settlement of the foundation; In slope protection engineering, the geotextile laid on the slope surface can constrain the displacement of soil particles, and together with anchor rods and grids, form a composite reinforcement system to prevent slope collapse and soil erosion. In addition, in temporary projects such as tunnels and foundation pits, geotextiles can also be used as temporary support materials to enhance construction safety.
The protective function mainly targets the protection of engineering structures and soil surfaces, effectively buffering external impacts and erosion. In river regulation projects, geotextile is laid on the surface of the embankment to resist water flow erosion and wind and wave erosion, protecting the soil on the embankment slope from being carried away; In road maintenance, geotextile can be used as a reinforcement material to delay the occurrence of road cracking and reflection cracks, and extend the service life of the road; In environmental engineering, it can also be used as a filter layer material to filter impurities in sewage and improve sewage treatment efficiency.
In summary, the multifunctionality of geotextiles makes them an indispensable geotechnical material in engineering construction. Different types of geotextiles (needle punched non-woven geotextiles, woven geotextiles, composite geotextiles, etc.) can be flexibly selected according to engineering needs, and the optimal engineering protection effect can be achieved through functional combinations.
Post time: Dec-19-2025