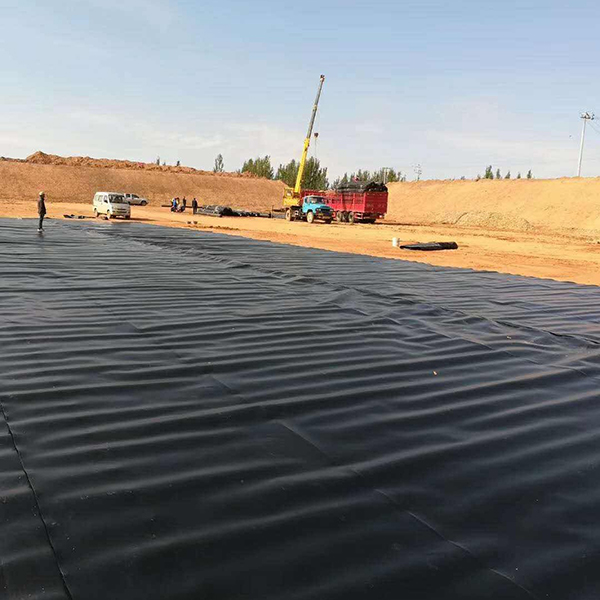
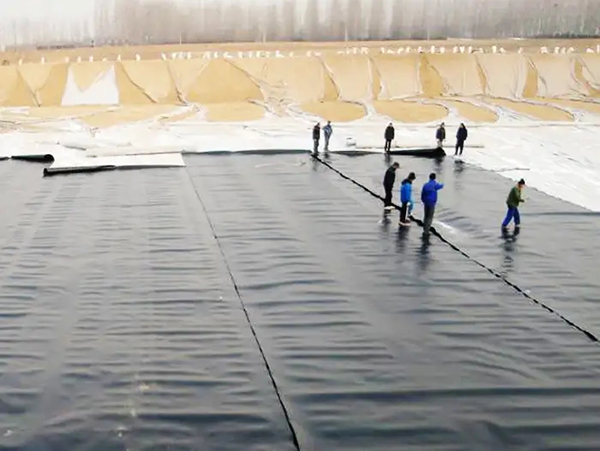
Geomembrane, as an impermeable thin film made of polymer synthetic materials, occupies an irreplaceable position in ecological governance, environmental restoration, engineering protection and other fields due to its excellent anti-seepage, isolation and reinforcement properties, and has become a key material in the modern governance technology system.
1、 The ‘anti-seepage barrier’ in the field of ecological restoration
In soil pollution control, geomembranes are the core means to curb the spread of pollutants. For example, in heavy metal contaminated sites, a closed isolation layer can be formed by laying geomembranes to prevent pollutants from infiltrating and polluting groundwater with rainwater, while providing a safe working environment for soil leaching, bioremediation, and other technologies. In mining reclamation, geomembranes can effectively isolate slag from surrounding soil and water bodies, prevent heavy metals and acidic wastewater from overflowing, and create basic conditions for vegetation restoration.
The anti-seepage effect of geomembranes is equally crucial in water treatment. In the treatment of urban black and odorous water bodies, geomembranes are laid at the bottom of the river to reduce water infiltration losses and block the release of sediment pollutants into the water. Combined with ecological shoreline protection technology, a composite treatment system of “anti-seepage+purification” is formed. In addition, in sewage treatment facilities such as artificial wetlands and oxidation ponds, geomembranes are used as lining materials to prevent the leakage of treated sewage from polluting groundwater sources and ensure the stability of treatment effects.
2、 The ‘safety cornerstone’ in the field of engineering protection
In hydraulic engineering, geomembrane is the preferred material for anti-seepage of dams and channels. Traditional earth dams are prone to dam failure due to leakage, but after laying geomembranes, the leakage can be reduced by more than 90%, significantly improving the safety of the dam. In channel engineering, geomembranes can reduce the loss of water resources during transportation, improve irrigation efficiency, and are particularly suitable for water-saving renovation in arid areas.
In transportation and municipal engineering, the isolation and reinforcement functions of geomembranes are indispensable. In the construction of highways and railways, laying geomembranes between the roadbed and the base layer can isolate soil of different particle sizes, prevent roadbed settlement and slurry overturning; In the construction of landfill sites, geomembranes serve as the core anti-seepage layer, which can prevent the leakage of leachate and work together with drainage systems to achieve harmless treatment of landfill waste. They are essential materials for the safe disposal of household waste and industrial solid waste.
3、 Technical Support for Agriculture and Ecological Construction
In the field of agriculture, geomembranes are used for anti-seepage of irrigation channels in high standard farmland, reducing water resource waste, preventing channel collapse, and extending project lifespan. In the treatment of saline alkali land, by laying geomembranes to block the upward channels of groundwater and combining with salt spraying measures, soil salinity can be quickly reduced, providing a suitable environment for crop cultivation.
In the construction of ecological corridors, geomembranes can be used for anti-seepage treatment of artificial lakes and wetland parks, maintaining the stability of water landscape while protecting the surrounding soil ecology. For example, in urban artificial water system engineering, geomembranes can accurately control water levels, avoid excessive water infiltration that affects surrounding building foundations, and balance ecological benefits and engineering safety.
In summary, geomembranes, through their core properties of anti-seepage, isolation, and reinforcement, have built efficient and stable technical barriers in pollution control, engineering protection, ecological restoration, and other fields. They are not only the “hardware support” for the implementation of treatment plans, but also the key guarantee for improving treatment efficiency and reducing long-term maintenance costs. Their position has become increasingly important with the improvement of environmental protection requirements and the upgrading of engineering technology.
Post time: Aug-20-2025