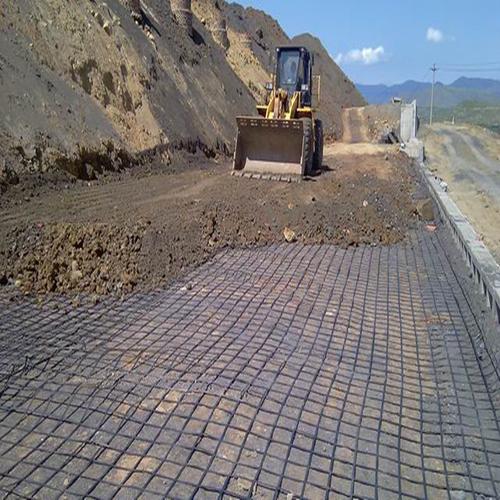
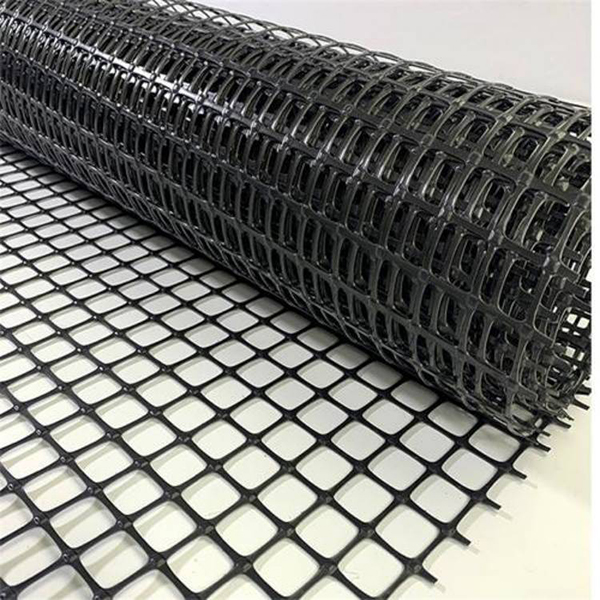
The selection of geogrid requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as project type, load, soil quality, environmental conditions, construction technology, and budget. The following are key points and suggestions:
Select type by project type
• Road engineering
Plastic geogrid: Suitable for roadbed reinforcement of general highways and rural roads, bi-directional plastic geogrid can be selected, with a bi-directional tensile strength of 15-30kN/m to meet the requirements.
Steel plastic geogrid: For highways and heavy-duty traffic roads, it is recommended to use steel plastic geogrids with specifications such as 80kN and 100kN.
Fiberglass geogrid: When used for reinforcing asphalt pavement, fiberglass geogrid can effectively prevent reflection cracks, and the mesh size of 12.7mm-25.4mm is commonly used.
Railway engineering: Steel plastic geogrids or polyester warp knitted geogrids are preferred, as they have high tensile strength and can withstand high-frequency loads from trains.
Water conservancy engineering: In the protection of dams and river slopes, drainage geogrids can effectively guide water flow and prevent soil infiltration and damage; Reinforced geogrids enhance the stability of the dam body.
Mining engineering: Reinforcement of tailings dams, slag yards, etc. requires the use of high-strength and corrosion-resistant geogrids, such as steel plastic geogrids or warp knitted polyester geogrids.
Select strength based on load
Light load transportation: For non motorized vehicle lanes, sidewalks, etc. on urban roads, low tensile strength geogrids such as polypropylene geogrid 50/30 models can be used.
Heavy load transportation: highways, railways, etc., calculate the required tensile strength based on the design load, generally requiring 80kN/m or more.
Select materials based on soil conditions
Soft soil: Plastic geogrids or steel plastic geogrids should be used for soft soil foundation reinforcement to enhance the bearing capacity of the foundation and reduce settlement.
• Sandy soil: Sandy soil is prone to liquefaction, and geogrids with good drainage performance, such as drainage geogrids, can be selected.
Clay: Clay has poor permeability, and reinforced geogrids can be used to improve the shear strength of the soil.
Select characteristics based on environmental conditions
Corrosion resistance: In coastal areas, chemical contaminated sites, etc., corrosion-resistant geogrids such as fiberglass geogrids and polyester geogrids should be selected.
• Aging resistance: For projects exposed to sunlight for a long time, the aging resistance of geogrids, such as polypropylene geogrids, should be considered.
• Frost resistance: For projects in cold regions, it is necessary to choose geogrids with good frost resistance, such as polyester geogrids.
Select structure according to construction technology
Welding type grille: The welding points have high strength and are suitable for large-sized mesh grilles, but attention should be paid to the welding quality during construction.
• Knitted grid: The knitted structure gives the grid high tensile strength and elongation, making it suitable for projects with high deformation requirements.
Stretch type grille: With high tensile strength, it is suitable for various soil conditions, but the price is relatively high.
Select products according to budget
• High cost-effectiveness: On the premise of meeting engineering requirements, choosing a cost-effective geogrid can be compared with multiple suppliers to select products with reliable quality and reasonable prices.
• Consider long-term costs: For projects that require a long service life, the long-term performance and maintenance costs of geogrids should be taken into account, and products with good durability should be selected.
Post time: Aug-08-2025