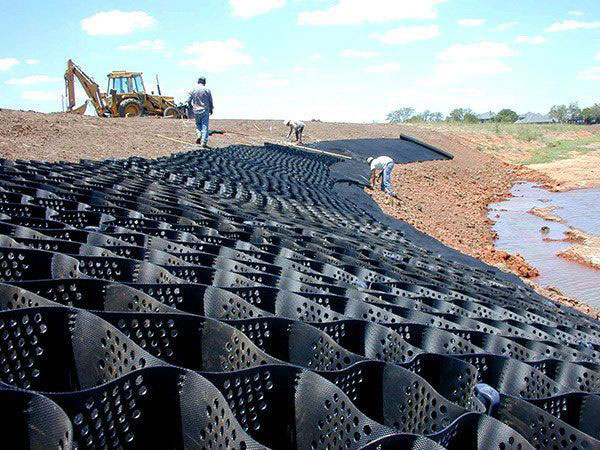
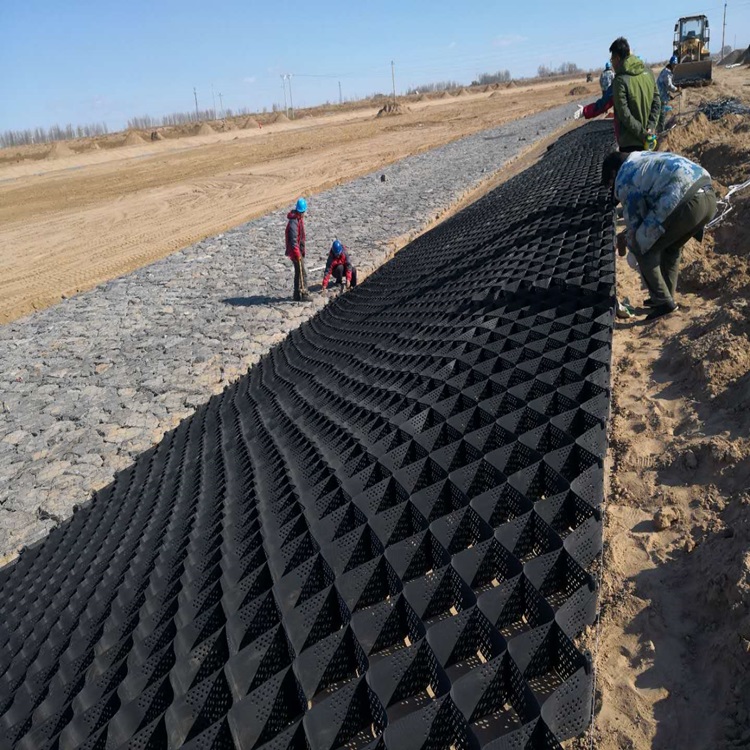
Geogrid protection is widely used in slope protection engineering due to its strong integrity and good ecological adaptability. Its standardized construction process directly determines the protection effect. The specific steps are as follows:
Construction preparation stage
Before construction, it is necessary to conduct on-site investigation and refine the plan, clarify the geological conditions of the slope, design slope and load requirements, and select the specifications of the geogrid (commonly 5-20cm in height), filling materials and fixing materials accordingly. At the same time, clean up the construction area, remove the slope and surrounding weeds, gravel, construction waste and other debris, check the stability of the slope, reinforce the loose parts in advance, and avoid collapse during construction. Prepare construction machinery (compactors, cutting machines, etc.) and materials to ensure that the geocell is undamaged, anchor bolt strength meets standards, filling materials (gravel, planting soil, etc.) meet grading and moisture content requirements, and temporary construction channels are built to ensure operational convenience.
Slope trimming process
Accurately adjust the slope according to the designed gradient, using manual and mechanical excavation methods to remove floating soil and weak interlayers, making the slope smooth and regular, with an error controlled within ± 5cm. After finishing, the slope soil should be compacted in a timely manner, and small compaction equipment should be used for layered rolling to ensure a compaction degree of not less than 85% and prevent later settlement and deformation. For steep slopes or loose soil slopes, geotextiles or geomembranes should be laid as anti-seepage and solid base layers. The overlap width of geotextiles should not be less than 15cm, and they should be fixed with anchor bolts to prevent displacement and form a stable base structure.
Fixed grid laying
Unfold the geogrid from top to bottom along the slope, ensuring that the grid axis is aligned with the slope direction and avoiding twisting and folding. After the grid is unfolded, immediately fix the edges and node positions with anchor bolts. The spacing between anchor bolts should be adjusted according to the slope height. When the slope height is ≤ 3m, the distance should be 1-1.5m, and when the slope height is>3m, the distance should be 0.8-1m. The depth of anchor bolts embedded in the soil should be ≥ 30cm to ensure firmness and reliability. The joint of the compartment is locked with dedicated connectors, with a minimum overlap length of 10cm, to ensure the integrity of the joint and prevent separation under stress.
Fill and compact the filling material
Fill the compartments with graded crushed stones or planting soil mixed with organic fertilizer in layers, with a filling thickness slightly 2-3cm higher than the height of the compartment, to avoid insufficient filling due to later settlement. After each layer of filling material is laid, a small compactor is used to roll along the grain direction of the grid, with a compaction degree of over 90%, ensuring that the filling material is dense and closely adheres to the grid to form a composite load-bearing structure. During the filling process, avoid direct mechanical crushing of the compartments to prevent damage and affect the protective effect.
Ecological greening and post maintenance
If designed as an ecological slope protection, after filling, cover the surface with 5-10cm of planting soil, choose vegetation varieties such as dogtooth roots and purple locust trees that are resistant to poverty and have developed root systems, plant them by sowing or transplanting, and cover them with non-woven fabric for moisture retention after sowing. Timely watering and maintenance should be carried out in the later stage to ensure the survival rate of vegetation. Regular inspections of the slope should be carried out to check whether the grid is loose and whether the filling material is lost. If any damage or settlement is found, it should be repaired and reinforced in a timely manner. During the rainy season, the drainage situation should be checked to avoid rainwater erosion causing slope instability and ensure the long-term stability of the geotechnical grid for slope protection.
Post time: Nov-26-2025