Complete Explanation of Composite Geomembrane Construction: Key Points and Precautions
Composite geomembrane, as an efficient anti-seepage material, is widely used in water conservancy, environmental protection and other engineering projects. The construction quality directly affects its anti-seepage effect and the long-term stability of the project, therefore, strict control of each link is required during the construction process.
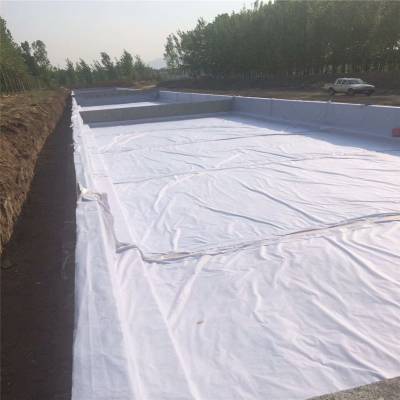
Preparation before construction is the crucial first step. Firstly, the laying surface should be treated to ensure that it is flat, compacted, and free of obvious spikes, stones, and other protrusions to avoid puncturing the geomembrane. At the same time, a detailed inspection of the composite geomembrane is required to check for any damages, holes, or other defects. If there are any issues, they should be promptly repaired or replaced. According to the engineering design requirements, accurately calculate the size and quantity of the required geomembrane, and arrange transportation and storage reasonably to avoid unnecessary damage to the geomembrane before construction.
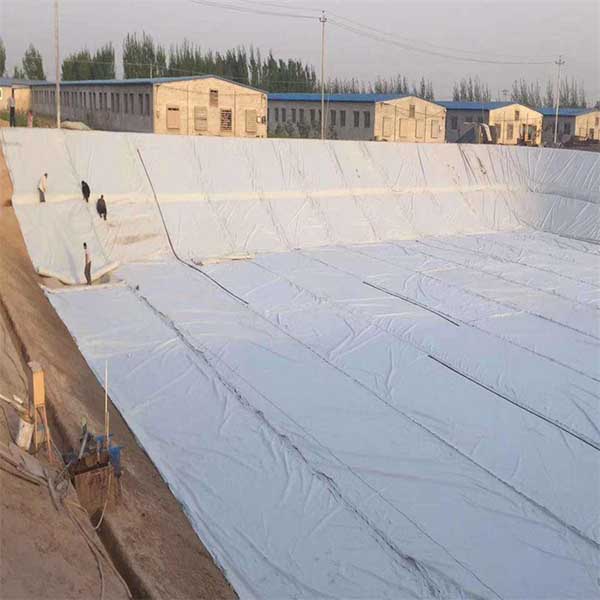
The laying process must follow certain principles and methods. Laying should be carried out from low to high, minimizing the number of joints and ensuring that the geomembrane is tightly adhered to the base surface to avoid hanging, wrinkling, and other phenomena. When laying, attention should be paid to reserving a certain amount of expansion and contraction to adapt to temperature changes and slight settlement of the foundation. In addition, construction personnel should wear soft soled shoes to avoid trampling damage to the geomembrane.
The splicing process is the core step of composite geomembrane construction, which directly affects the anti-seepage effect. The commonly used splicing methods currently include hot welding and adhesive bonding. Hot welding is widely used, and its principle is to use professional welding equipment to heat the edges of the geomembrane to a molten state, and then apply pressure to fuse them together. Before welding, it is necessary to adjust the equipment parameters and determine the appropriate temperature, speed, and pressure based on the thickness and material of the geomembrane. During the welding process, it is necessary to check the welding quality at all times to see if there are any issues such as missed welding or virtual welding. Every completed welding section should undergo on-site inflation testing to ensure the sealing of the welding seam.
After the composite geomembrane is laid, the protective layer construction should be carried out in a timely manner. The protective layer material can be selected from clay, sand, gravel, etc., and the thickness should meet the design requirements. During construction, attention should be paid to avoiding damage to the already laid geomembrane. Manual or small machinery should be used for laying and compaction to ensure that the protective layer is uniform and dense. Corresponding protective measures should also be taken in subsequent processes such as earthwork backfilling and concrete pouring to prevent construction machinery, tools, etc. from scratching the geomembrane.
Quality control during the construction process is crucial. Set up dedicated quality inspectors to conduct strict inspections on each process, promptly identify and solve problems. Make good construction records, including material entry inspection, laying process, splicing quality inspection results, etc., to provide a basis for project acceptance and later maintenance. Only by strictly controlling every aspect of the construction of composite geomembranes can the anti-seepage effect and long-term stable operation of the project be ensured.
Post time: May-05-2025