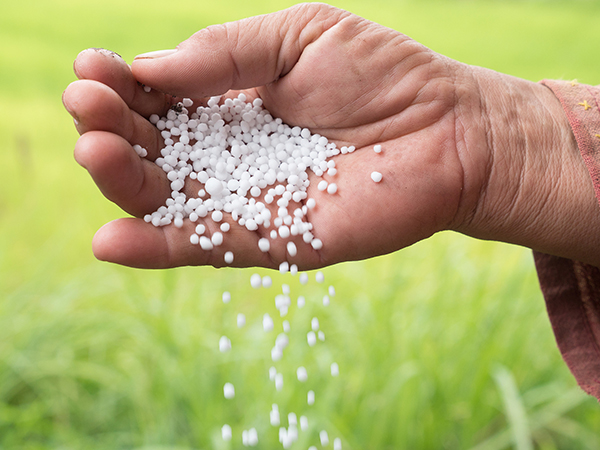
The application of urea in agriculture is mainly reflected in two aspects: fertilizer and related agricultural chemical preparations, among which nitrogen fertilizer application is the most core. Below, we will explain the mechanism of action, application method, precautions, and supporting technologies.
1、 The main mechanism of action of urea in agriculture
Urea has a nitrogen content of about 46% and is the most commonly used solid nitrogen fertilizer with the highest nitrogen content. After being applied to the soil, it gradually hydrolyzes under the action of urease to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide. Ammonia is further converted into ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen, which are absorbed and utilized by crop roots. Nitrogen is an important element that constitutes proteins, chlorophyll, and various enzymes. The application of urea can significantly promote crop stem and leaf growth, enhance photosynthesis, and improve yield and quality. Compared with other nitrogen fertilizers, urea has the advantages of high nitrogen content, good physical properties, easy storage and transportation, and no significant acidification effect on soil. It is currently one of the most widely used nitrogen fertilizers in countries around the world.
2、 The main application methods of urea in agriculture
1. Application as base fertilizer
Base fertilizer is a fertilizer applied to the soil before sowing or planting, with the aim of providing stable nutrients for the entire growth period of crops. When urea is used as a base fertilizer, it is generally applied in combination with organic fertilizer, phosphorus fertilizer, and potassium fertilizer to achieve nutrient balance.
Application points:
Usually, it is necessary to apply a depth of about 10 centimeters and cover it with soil to avoid exposure to the surface and loss of ammonia volatilization;
Dryland can be cultivated by strip, hole, or scattered application followed by plowing;
Waterfields can be applied after plowing and before transplanting, and mixed with harrowing.
2. Apply as topdressing
Topdressing is one of the most common uses of urea in agriculture, which is applied during the growth period of crops according to their growth and fertilizer requirements.
• Rice: Fertilization is often applied in stages of tillering, jointing, and booting to promote tillering, enhance lodging resistance, and improve seed setting rate;
Wheat and corn: focus on key growth stages such as greening, jointing, and bell mouth stage for topdressing;
Vegetables and fruit trees: Use small quantities multiple times to avoid excessive one-time use that may cause root burning or excessive growth.
The main application methods are trench and hole application, followed by soil covering or watering to improve utilization efficiency.
3. Spraying foliar fertilizer
Urea is easily soluble in water and has a small molecular volume. It can enter the plant through leaf stomata and cuticle, and has a fast effect. It is a commonly used foliar fertilizer material.
Applicable situation:
• Significant nitrogen deficiency symptoms in crops, such as yellowing of leaves and stunted growth of plants;
The later stage of decline in root absorption capacity, such as during rice grain filling and before and after fruit harvesting in fruit trees;
Some economic crops require rapid nitrogen supplementation to improve quality, such as cotton, rapeseed, etc.
Key points for use:
The general spraying concentration is 0.2% to 1%, which varies depending on the crop type and growth period;
Choose cloudy or evening spraying to avoid leaf burns caused by high temperature and strong light;
Can be sprayed in combination with potassium dihydrogen phosphate, trace elements, etc. to achieve comprehensive nutrition.
4. As raw materials for compound fertilizers and formula fertilizers
Urea can be mixed with basic fertilizers such as ammonium phosphate and potassium chloride in a certain proportion to produce various formulas of compound fertilizers and specialty fertilizers, such as rice specialty fertilizer, corn specialty fertilizer, fruit tree specialty fertilizer, etc. Through scientific formulas, it is possible to balance the supply of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements, meet the needs of different crops and soils, and improve fertilization efficiency.
Post time: Dec-16-2025