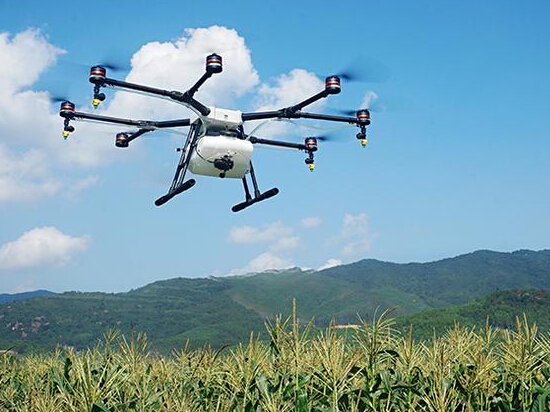
The core application of agricultural drones is to solve the problems of insufficient labor, high cost, and low efficiency in traditional agriculture through efficient and precise operations, mainly focusing on five areas: plant protection, sowing, fertilization, monitoring, and irrigation.
1. Plant Protection Operations (Core Application)
This is the most mature and widely used application scenario for agricultural drones, mainly for spraying pesticides and foliar fertilizers.
• Advantages: Compared with the manual spray, the operating efficiency is 10-20 times higher (the daily average operating area of a single machine can reach 100-300 mu); By using GPS positioning for precise spraying, pesticide usage can be reduced by 15% -30%, avoiding waste and environmental pollution; It can also enter areas with hills and tall crops (such as corn and sugarcane) that are difficult to reach manually, reducing the risk of poisoning for workers.
Applicable scenarios: Prevention and control of pests, diseases, and weeds in various crops such as rice, wheat, cotton, fruits, and vegetables.
2. Sowing and Fertilization
Replace some manual or mechanical operations, suitable for planting and nutrient supply of various crops.
Sowing: mainly used for sowing small particle seeds such as rice live broadcast, vegetable seeds, grass seeds, etc. By adjusting the speed of the sowing disc to control the sowing density, the operating efficiency is 8-15 times that of manual labor, and the sowing uniformity is higher.
Fertilization: It is divided into solid fertilizer (such as compound fertilizer, organic fertilizer granules) and liquid fertilizer (such as water-soluble fertilizer) sowing. The amount can be precisely controlled according to the growth stage of crops (such as wheat jointing stage, fruit tree swelling stage), avoiding the problem of uneven fertilization in traditional methods.
3. Farmland monitoring and inspection
By carrying different sensors, real-time monitoring of crop growth, soil conditions, pests and diseases can be achieved, providing data support for accurate management.
Crop growth monitoring: Equipped with visible light cameras, capture the color and density of crop leaves, analyze whether the growth is uniform, and promptly detect problems such as fertilizer deficiency and drought.
Disease and pest warning: By capturing subtle changes in crop leaves through multispectral cameras (such as chlorophyll loss caused by diseases and pests), diseases and pests can be detected earlier than manually, achieving “early prevention and control, less medication”.
Soil and environmental monitoring: In conjunction with soil sensor data, monitor soil moisture and fertility, and plan irrigation and fertilization plans based on drone captured land images.
4. Auxiliary irrigation
Mainly used in areas with drought or insufficient irrigation conditions to assist in achieving precise water replenishment.
Some drones can be equipped with small water tanks to provide emergency water replenishment for locally arid areas, such as hilly slopes and scattered small farmlands; More often than not, drones generate irrigation demand maps by monitoring soil moisture and crop wilting, guiding ground irrigation equipment (such as drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation) to operate accurately and avoid blind irrigation.
5. Other auxiliary applications
Crop yield estimation: By capturing images of the mature stage of crops and combining them with AI algorithms to calculate the number of spikes and fruits, the yield is estimated, providing a basis for harvest planning and market sales.
• Farmland surveying: Quickly draw high-definition maps and slope maps of land parcels to help farmers plan planting layouts (such as dividing different crop planting areas), or provide surveying data for land transfer and agricultural project applications.
Disaster assessment: After disasters such as floods, hail, typhoons, etc., drones can quickly survey the area and degree of crop damage, help farmers assess losses in a timely manner, apply for insurance claims, and develop replanting or remedial plans.
Post time: Sep-25-2025