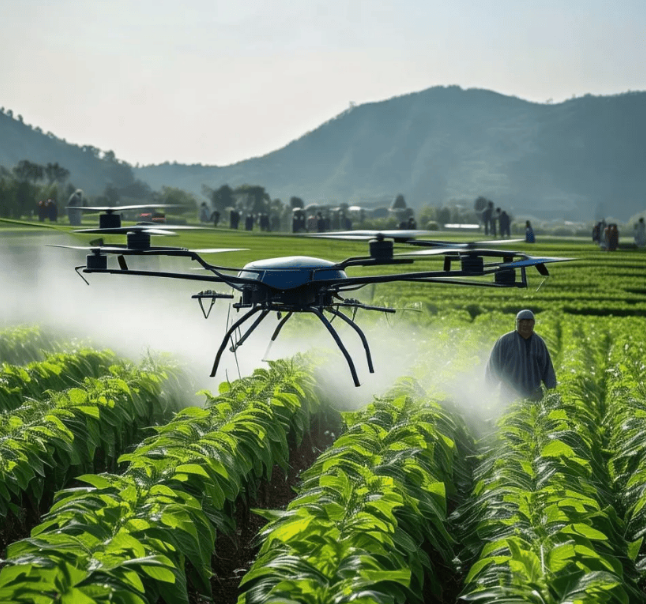
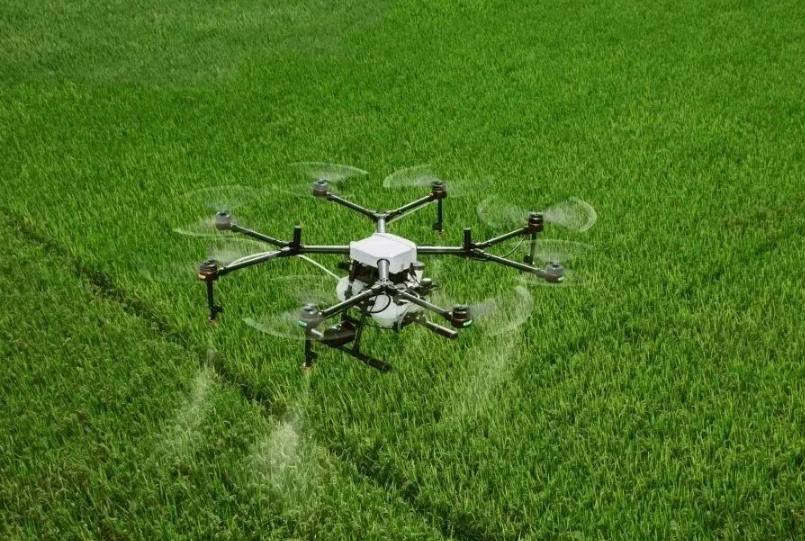
In the current era of accelerating the implementation of “smart agriculture”, agricultural drones have been upgraded from “auxiliary tools” to “main production forces”. Their advantages are deeply tailored to the needs of farmers and the pain points of agricultural development, completely changing the traditional farming model.
Firstly, ultimate efficiency can solve the “employment dilemma”. Traditional artificial crop protection has a daily operation area of only 10-15 acres and is greatly affected by physical and weather conditions, while a mainstream agricultural drone can operate on an area of 200-500 acres per day, with an efficiency 20-30 times that of manual labor. At critical junctures such as spring plowing and autumn harvest, drones can achieve continuous operation with “people resting and machines not resting”, especially for large-scale planting bases, which can quickly complete comprehensive plant protection and avoid yield reduction caused by agricultural delays. At the same time, it also solves the core pain point of “difficult and expensive employment” in rural areas. In the past, it took 10 people to cooperate for 3 days for a hundred acres of farmland, but now one person can operate one drone in one day, greatly reducing labor costs.
Secondly, precise homework achieves “cost reduction and quality improvement”. By relying on GPS positioning, millimeter wave radar, and intelligent flight control systems, agricultural drones can achieve centimeter level route planning, with a uniformity error of no more than 5% in drug spraying, and can accurately control the amount of pesticides and fertilizers used per acre of land. Data shows that compared to manual spraying, drones can reduce pesticide use by 15% -30%, which not only lowers the cost of agricultural inputs for farmers, but also reduces the pollution of soil and water sources by chemical agents. In fruit tree cultivation, drones can also use variable spraying technology to adjust the concentration of pesticide according to the growth of fruit trees, improve fruit quality and yield, and achieve “reduction without reduction in efficiency, improvement in quality and increase in income”.
Thirdly, the “super adaptability” to adapt to complex scenarios. Traditional farming is difficult and risky in complex terrains such as mountains, hills, and terraced fields, while agricultural drones can flexibly respond to various types of land – whether it is mountainous orchards with a slope of more than 30 degrees, or contiguous rice and cotton fields, they can complete blind spot operations by adjusting their flight height and speed. Some models also have a “fully autonomous obstacle avoidance” function, which can automatically avoid obstacles such as trees and power poles, ensuring operational safety in complex field environments and filling the gap in mechanized operations in complex terrains.
Fourthly, data empowerment promotes “scientific planting”. Modern agricultural drones are not only “work tools”, but also “data collection terminals”. Drones equipped with multispectral cameras and infrared sensors can quickly obtain data on vegetation coverage, crop growth, pest and disease distribution in farmland, and generate visual reports through backend algorithms. Farmers can accurately grasp the “health status” of each field without the need for on-site inspections, such as identifying the affected areas of pests and diseases in advance, achieving “early detection and prevention”; It is also possible to adjust the fertilization plan based on crop growth data, avoiding blind input and making planting more scientific.
Fifth, convenient operation reduces the “threshold for use”. Nowadays, agricultural drones have achieved “foolproof operation” without the need for professional flying experience. Farmers can complete route planning, parameter settings, and start operations with just one click through a mobile app. Some brands also provide integrated services of “pilot training+after-sales maintenance” to address farmers’ operational and maintenance concerns. At the same time, the body design of the drone is lightweight, and after folding, it can be easily placed in the trunk of a car, making it convenient to transport between different plots and meeting the “small and flexible” usage needs of farmers.
From efficiency improvement to cost reduction, from precise operations to data empowerment, agricultural drones are becoming the “air engine” driving agricultural modernization with multidimensional advantages, allowing more farmers to enjoy the convenience and dividends brought by technology.
Post time: Oct-22-2025